Different Theories That Explain the Formation of Organic Molecules
2021 Scientists have recreated the reaction by which carbon isotopes made their way. Approximately of the first large organic molecules to form and self-replicate were RNA molecules with DNA molecules starting much later.
D1 Origins Of Life On Earth Bioninja
Study of structure determines their structural formulaStudy of properties includes physical and chemical properties and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior.
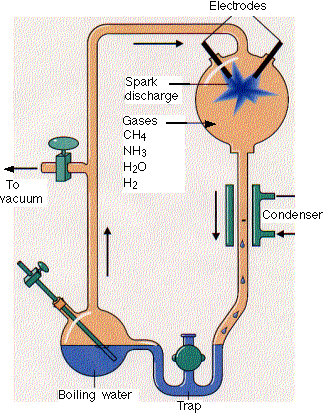
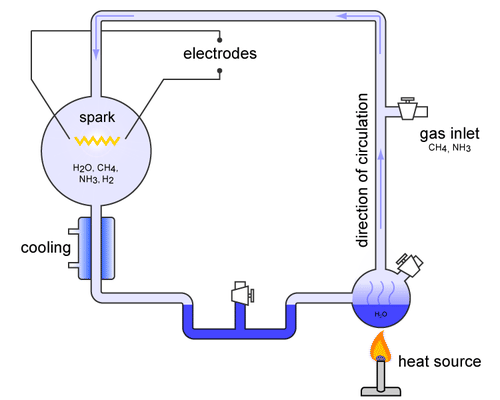
. They are small simple compounds that play important roles in the cell although they do not form cell structures. In 1952 Stanley Miller and Harold Urey performed the MillerUrey experiment demonstrating how organic molecules could have spontaneously formed from inorganic precursors under conditions like those posited by the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis. Second these small monomers combined to form larger and more complex polymers.
Functional groups combine with the chain to form biomolecules. Cairns-Smith suggests that mineral crystals in clay could have arranged organic molecules into organized patterns. This drawing method is essential because the placement of different atoms could yield different molecules even if the molecular formulas were exactly the same.
Replicating molecules evolved and began to undergo natural selection. They do not possess hydrogen or oxygen and their derivatives. Organic Compounds Inorganic Compounds.
Many new synthetic methods reaction mechanisms analytical techniques and structural theories have been developed. Many biologically relevant macromolecules are formed by linking together a great number of identical or very similar smaller organic molecules. Organic compounds are characterized by the presence of carbon atoms in them.
Carbon chains form the skeletons of most organic molecules. In living systems large organic molecules called macromolecules can consist of hundreds or thousands of atoms. Functional groups combine with the chain to form biomolecules.
Below are two drawings of a 4-carbon molecule with two chlorines and two. Pure carbon compounds such as diamond and. The atoms of an organic molecule are typically organized around chains of carbon atoms.
Inorganic compounds make up 115 of a living cells mass. Carbon chains form the skeletons of most organic molecules. Noticeable exceptions are carbon monoxide CO carbon dioxide CO 2 carbonates eg.
However they were never able to duplicate the conditions themselves. Experiments suggest that organic molecules could have been synthesized in the atmosphere of early Earth and rained down into the oceans. Most macromolecules are polymers molecules that consist of a single unit monomer repeated many times.
Organic molecules could have shaped instinctively in Earths early atmosphere and lesser molecules could promise together to shape big organic molecules. Previous scientists such as Oparin and Haldane had hypothesized that organic molecules could be created from inorganic molecules that could be found in the atmosphere of the young Earth. According to this view the mitochondria and other organelles were once bacteria that were internalized by another larger cell.
Organic compounds consisting of hydrogen oxygen carbon and their other derivatives. A widely used way of showing the 3D structure of molecules is the use of dashes wedges and straight lines. After a while organic molecules took over this job and organized themselves.
Organic compounds are those that have carbon atoms. Many biologically relevant macromolecules are formed by linking together a great number of identical or very similar smaller organic molecules. Lynn Margulis 1938- proposed the endosymbiont hypothesis to explain the origin of organelles including the mitochondria.
Calcium carbonate carbides eg. Most of the carbon found in organic molecules originates from inorganic carbon. Four of carbons six electrons are available to form bonds with other atoms.
Formation of organic molecules the building blocks of cells eg amino acids nucleotides simple sugars formation of polymers longer chains of organic molecules that can function as enzymes to carry out metabolic reactions encode hereditary information and possibly replicate eg proteins RNA strands. An organic molecule is one which contains carbon although not all compounds that contain carbon are organic molecules. Dehydration reactions typically require an investment of energy for new bond formation while hydrolysis reactions typically.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure properties and reactions of organic compounds which contain carbon-carbon covalent bonds. Organic chemistry developed into a productive and exciting science in the nineteenth century. The discovery validates theories of the formation of organic compounds in extraterrestrial environments.
Most inorganic compounds do not have carbon atoms in them some exceptions do exist 2. First small organic molecules - such as amino acids which make proteins and nucleotides which make DNA - were made. Calcium carbide and cyanides eg.
Understanding about the structures of organic chemistry began with a theory of bonding called valence theory Kekule Couper 1858. The study of organic reactions. Because these biomolecules are typically large we call them macromolecules.
Their theories and discoveries served as the foundation from which further advancements occurred including the distinction between atomic and equivalent weights the structural theory and the tetrahedral nature of carbon. RNA and DNA molecules the genetic material for all life are just long chains of simple nucleotides. Because these biomolecules are typically large we call them macromolecule s.
Dehydration and hydrolysis reactions are similar for all macromolecules but each monomer and polymer reaction is specific to its class.
D1 Origins Of Life On Earth Bioninja
First Organic Molecules And The First Cell Study Guide Inspirit

Abiogenesis Theory Experiments Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
No comments for "Different Theories That Explain the Formation of Organic Molecules"
Post a Comment